🐒 最近看了Mixtral是如何实现MoE的,发现代码写的是真的简洁优雅,下面来详细解读一下~
1. 源码
class MixtralSparseMoeBlock(nn.Module):
"""
This implementation is
strictly equivalent to standard MoE with full capacity (no
dropped tokens). It's faster since it formulates MoE operations
in terms of block-sparse operations to accommodate imbalanced
assignments of tokens to experts, whereas standard MoE either
(1) drop tokens at the cost of reduced performance or (2) set
capacity factor to number of experts and thus waste computation
and memory on padding.
"""
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.hidden_dim = config.hidden_size
self.ffn_dim = config.intermediate_size
self.num_experts = config.num_local_experts
self.top_k = config.num_experts_per_tok
# gating
self.gate = nn.Linear(self.hidden_dim, self.num_experts, bias=False)
self.experts = nn.ModuleList([MixtralBlockSparseTop2MLP(config) for _ in range(self.num_experts)])
# Jitter parameters
self.jitter_noise = config.router_jitter_noise
def forward(self, hidden_states: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
""" """
batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_dim = hidden_states.shape
if self.training and self.jitter_noise > 0:
hidden_states *= torch.empty_like(hidden_states).uniform_(1.0 - self.jitter_noise, 1.0 + self.jitter_noise)
hidden_states = hidden_states.view(-1, hidden_dim)
# router_logits: (batch * sequence_length, n_experts)
router_logits = self.gate(hidden_states)
routing_weights = F.softmax(router_logits, dim=1, dtype=torch.float)
routing_weights, selected_experts = torch.topk(routing_weights, self.top_k, dim=-1)
routing_weights /= routing_weights.sum(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
# we cast back to the input dtype
routing_weights = routing_weights.to(hidden_states.dtype)
final_hidden_states = torch.zeros(
(batch_size * sequence_length, hidden_dim), dtype=hidden_states.dtype, device=hidden_states.device
)
# One hot encode the selected experts to create an expert mask
# this will be used to easily index which expert is going to be sollicitated
expert_mask = torch.nn.functional.one_hot(selected_experts, num_classes=self.num_experts).permute(2, 1, 0)
# Loop over all available experts in the model and perform the computation on each expert
for expert_idx in range(self.num_experts):
expert_layer = self.experts[expert_idx]
idx, top_x = torch.where(expert_mask[expert_idx])
# Index the correct hidden states and compute the expert hidden state for
# the current expert. We need to make sure to multiply the output hidden
# states by `routing_weights` on the corresponding tokens (top-1 and top-2)
current_state = hidden_states[None, top_x].reshape(-1, hidden_dim)
current_hidden_states = expert_layer(current_state) * routing_weights[top_x, idx, None]
# However `index_add_` only support torch tensors for indexing so we'll use
# the `top_x` tensor here.
final_hidden_states.index_add_(0, top_x, current_hidden_states.to(hidden_states.dtype))
final_hidden_states = final_hidden_states.reshape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_dim)
return final_hidden_states, router_logits
2. 解读
- 输入hidden_states的形状是(batch, sequence_length, hidden_dim), 我们以(2, 10, 128)为例(n_experts=8, top_k=2):
- 首先将hidden_states view成(batch * sequence_length, hidden_dim), 即:(20, 128) –> 1个batch有20个tokens, 每个token的embedding维度是128
- 接着将hidden_states传入gate门控网络(就是一个简单的线性层), 输出形状是(20, 8), 然后对这个张量进行softmax,让每一行的和为1,将其作为routing_weights –> 每一个token, 8个专家对其处理的能力
- 然后使用torch.topk函数将routing_weights每一行最大的两个权重值以及对应的索引拿出来,分别作为新的routing_weights和selected_experts,他们的形状均为(20, 2), 这样,我们选择哪两个专家,以及这两个专家的权重就确定下来了,后面也对新的routing_weights重新进行了一下softmax,让两个专家的权重和为1
- 接着,初始化一个形状为(20, 128)的全0张量,用于存储计算结果
🧐 其实到这里,一切都还是比较容易理解的,后面初始化的一个expert_mask,直接给我干懵了 ,其实只要理解了expert_mask每个元素的含义,后面就比较好理解了~
- 在permute之前,expert_mask的形状是(20, 2, 8),这个还是比较容易理解的,就是对每个专家进行了一下one-hot编码,如下图:
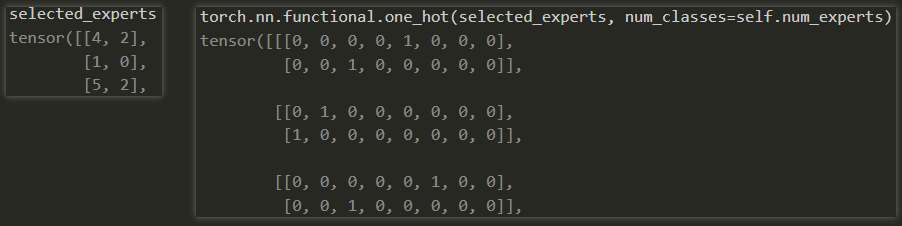
- permute之后,expert_mask的形状变成了(8, 2, 20), 如下图:
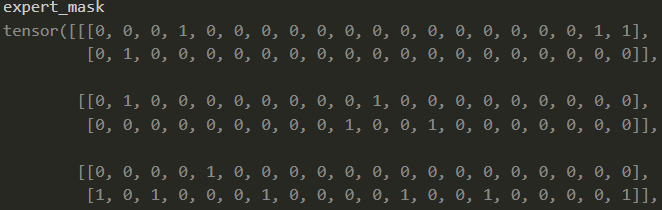
🎄 我们可以这样理解:以第一个专家为例,它的形状是(2, 20),每一行可以视为第top1和第top2个专家,每一列代表的就是一个token,第二列是[0, 1],代表的就是第二个token会被第一个专家处理,且第一个专家是作为这个token的第top2个专家
- 后面就是遍历每一个专家,取出这个专家需要处理的tokens (top_x),以及这个专家是作为每个token的第top几个专家 (idx)
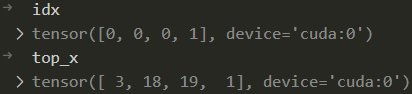
- 在确定了每个专家会处理哪些tokens后,在forward的时候,只需要从hidden_states中取出需要处理的tokens的embedding,传入对应的专家网络即可:
current_state = hidden_states[None, top_x].reshape(-1, hidden_dim)
current_hidden_states = expert_layer(current_state) * routing_weights[top_x, idx, None]
🧐 看到这里,一切都明朗了,写的真的很精彩,Mixtral选择遍历每个专家,而不是每个token,极大减小了时间复杂度,也是学习到了~
3. 练习
- 尝试将huggingface bert的FFN层换成MoE架构